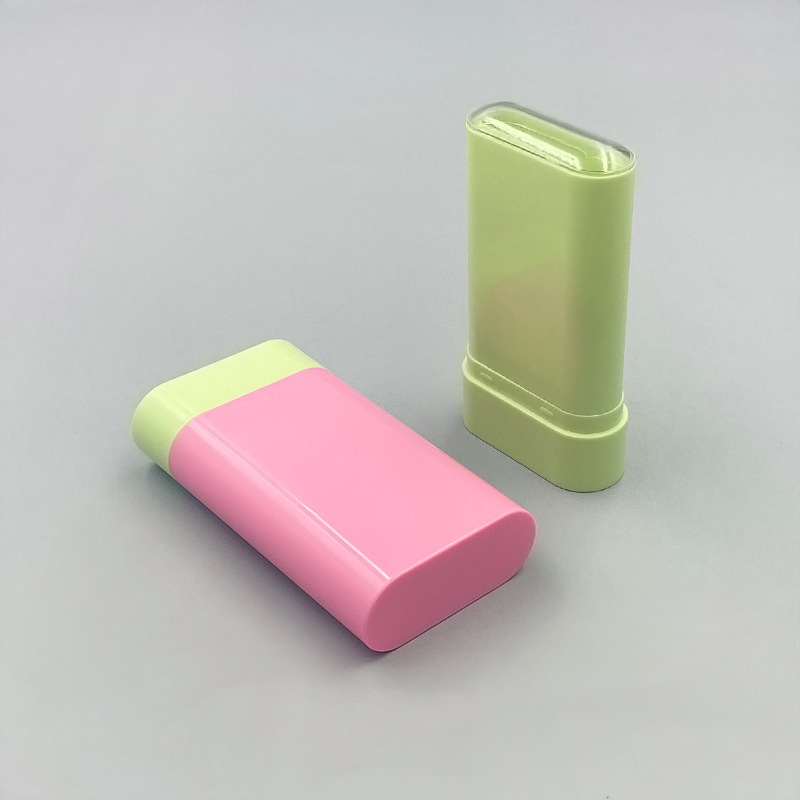
Pumpa za pjenu je dozator koji radi pritiskom tekućeg sadržaja zajedno sa zrakom kako bi se stvorila pjena. Obično se koriste u pakiranju proizvoda kao što je sapun za ruke, sredstva za čišćenje, i razna sredstva za pranje.

Struktura pjenastih pumpi
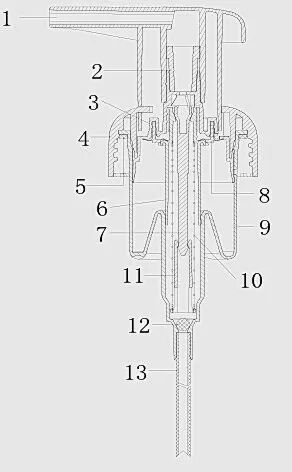
Pumpa za pjenu, gledano po unutarnjoj strukturi, prvenstveno se sastoji od pet ključnih dijelova.
- Pokretač, koji funkcionira prijenosom sile pritiska korisnika na ostale unutarnje komponente, a koji, zajedno s proljećem, olakšava ciklus pritiska i vraćanja za doziranje. Dizajn i boja glave aktuatora mogu se prilagoditi prema potrebi.
- Tekuća komora , koji istiskuje sadržanu tekućinu tijekom pritiska prema dolje i usisava tekućinu iz boce u komoru tijekom odskoka; unutarnja opruga također osigurava potrebnu povratnu silu ovdje.
- Zračna komora, koji uvlači i izbacuje zrak.
- Dip Tube, koji služi kao veza između tekućine u boci i mehanizma pumpe, djelujući kao kanal za ulazak tekućine u komoru za tekućinu i osiguravajući brzo doziranje s minimalnim ostacima.
- Komora za miješanje zraka i tekućine, gdje se tekućina i zrak iz svojih odgovarajućih komora temeljito miješaju i pod pritiskom tijekom pritiska prema dolje. Ova smjesa zatim prolazi kroz sito s gustom mrežom unutar komore za miješanje kako bi se stvorila finoća, nježna pjena.
Principi rada pumpi za pjenjenje koje se mogu vidjeti na tržištu općenito su isti. U usporedbi s tradicionalnim losionima na pumpice, cjelokupna struktura pumpe za pjenu je relativno složenija, prvenstveno zato što uključuje dodatnu zračnu komoru. Sama pumpa je temeljna radna komponenta cijelog proizvoda, određivanje ispuštenog volumena, kvalitetu pjene, i dosljednost performansi pumpe.
Tijekom korištenja, pritiskom na glavu pokretača pokreće veliki klip, mali klip, i povezane komponente prema dolje, nanošenje opterećenja na oprugu. Istovremeno, kuglasti ventil je zatvoren. Tekućina unutar komore za tekućinu se istiskuje kako se volumen komore smanjuje, putujući uz kanal tekućine. Ova tekućina se miješa sa zrakom koji se istovremeno izbacuje iz zračne komore kroz sito s finom mrežicom.
Surfaktanti tekućine miješaju se sa zrakom i stvaraju pjenu, koji se zatim izbacuje kroz mlaznicu. Kada se glava aktuatora otpusti, opruga gura klip prema gore. To stvara podtlak unutar komore za zrak i komore za tekućinu. Otvara se ventil za dovod zraka, dopuštajući zraku da uđe u zračnu komoru, dok se kuglasti ventil otvara, omogućujući izvlačenje tekućine iz boce kroz uronjenu cijev u komoru za tekućinu.
Ovaj ciklus se ponavlja sa svakim aktiviranjem.
Ruispack pruža različite vrste raspršivača okidača koje su za različite svrhe, Pronađite ono što želite u nastavku https://www.ruispack.com/product-category/plastic-bottles-jars/foamer/



